Innovative Propulsion: How Solar Sails Could Revolutionize Space Exploration
Solar sails represent a transformative approach to space exploration, utilizing the constant pressure of sunlight for propulsion, much like sailboats use wind. This innovative technology, as detailed by astrobiologist Manasvi Lingam from the Florida Institute of Technology, could provide a cost-effective method for probing the outer reaches of our solar system. By harnessing the momentum of light particles that strike the sails, these spacecraft can achieve high speeds without the burden of carrying fuel, offering a potential solution for long-duration missions to distant celestial bodies.
Targeting Icy Moons: The Potential for Discovering Life
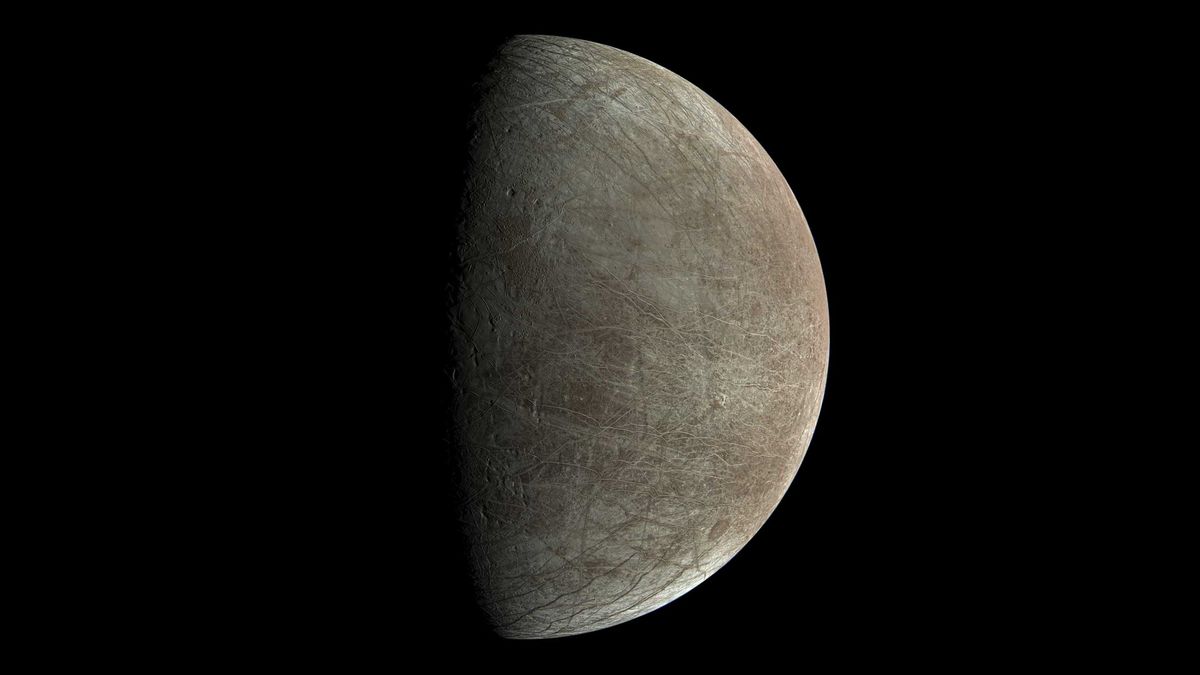
Europa and Enceladus, two moons orbiting Jupiter and Saturn respectively, are prime candidates for this type of exploration due to their subsurface oceans, which are thought to potentially harbor life. The intrigue surrounding these moons is heightened by phenomena such as Enceladus’s watery geysers, which eject what could be biologically rich materials into space. A solar-sailing probe could efficiently sample these plumes to analyze for life-sustaining molecules like amino acids, providing insights into the biological makeup of these alien waters without the need to penetrate their icy crusts.
The Future of Interstellar Travel and Challenges Ahead
The practicality of solar sails extends beyond our solar system. Projects like the Breakthrough Starshot initiative envision using light sails propelled by lasers to reach neighboring star systems within decades, a concept that could mark the beginning of interstellar exploration. However, challenges such as controlling the speed to safely sample high-velocity space plumes without destroying delicate molecular structures need to be addressed. As solar sail technology continues to develop, it promises not only to expand the boundaries of human exploration but also to enhance our understanding of potentially habitable environments beyond Earth.